Practice Worksheet Graphing Quadratic Functions In Standard Form Key – If you’re looking for graphing functions worksheets, you’ve come to the right place. There are several different types of graphing functions to choose from. Conaway Math offers Valentine’s Day-themed worksheets with graphing functions. This is a great way for your child to learn about these functions.
Graphing functions
To analyze data and create graphs, graphing functions worksheets can be used. Students will be able to use graphing functions worksheets in order to solve problems and compare data. They will also learn about the different types of graphs. Some worksheets are focused on graphing inverse relations and functions. One worksheet may show the graphs for a function while another shows graphs for a function and its inverse.
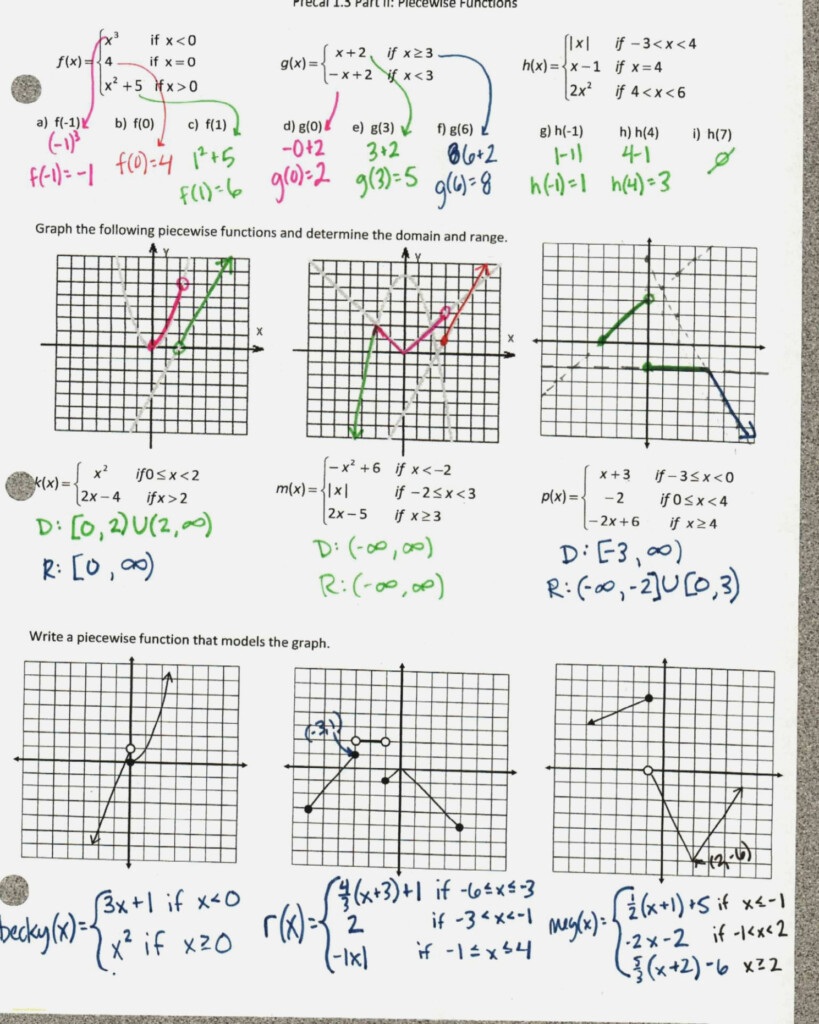
The first step in graphing a function is to identify the x-intercept and y-intercept of the function. Then, students must complete the input-output table. They will then graph the function.
How to identify their shape
One of the first steps to graphing functions is to identify their shapes. Functions generally have positive values. If x=2, then the graph of function f(x), will take positive value. If x=1, then the graph graph of function k(x), will take negative value.
Different functions can have graphs with similar shapes. However, they may have different shapes. A graph of a function can be identified by its domain, range and x-intercepts. You can then use this graph to calculate the values of the function.
Identifying their properties
Two basic properties of graphing functions are a domain (or range) and a range (or range). A real function has a domain and range of R. For example, y=3x is a real function. One-to-one functions have one output value for every input value.
Continuous functions have no jumps in their graph; instead, the values of continuous functions approach the value x at each point. Open intervals are the opposite. An open interval is one that extends from negative to positive. A graphing function may have multiple intervals of its domain.
An odd function has an inverse when x is replaced with a negative number. Its inverted form is f(x). A trigonometric sine function is an example of an odd function. It is also called a cosecant or trigonometric sine function. Graphing a linear function using a computer algebra system is an effective way to explore the properties of a function. You can then model the function by building a computational model of it.
Identifying their asymptotes
When graphing functions, it is important to identify their asymptotes. The horizontal asymptote is a function whose denominator equals zero. You should search for a vertical asymptote if the denominator does not equal zero. You should avoid this type if possible. You can identify horizontal asymptotes by performing a highest order term analysis.
The point at which a function reaches its maximum value is called the asymptote. This will cause the graph to be either vertical or horizontal. Horizontal asymptotes are marked with vertical dashed lines. If you graph a function that has a zero numerator, it can lead to asymptotes that are so close together that it is hard to tell the difference.
Graphing a rational function is similar to graphing a linear function. It will be necessary to compare the denominator’s degree with that of the numerator.
Identifying their vertex
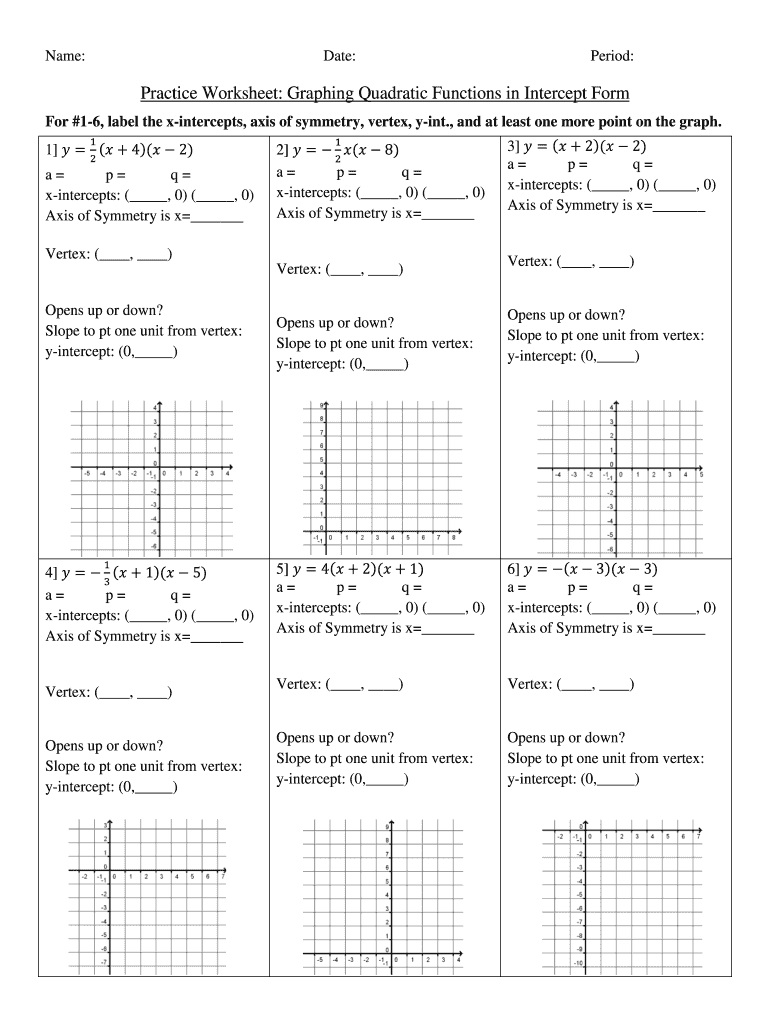
Students need to identify their vertex in order to comprehend a graphing function. Students must be able to determine the vertex of a graph by its x and y values. The point at which the x- and y-values meet is called the vertex of a parabola.
Students must identify the vertex when graphing quadratic functions. Then, they must convert the quadratic function’s standard form to its vertex form. They should also be able to locate the zeros in the quadratic functions. These graphing worksheets help students understand quadratic functions.